
Draw the Lewis electron structure of the molecule or polyatomic ion.Using this information, we can describe the molecular geometry The arrangement of the bonded atoms in a molecule or a polyatomic ion in space., the arrangement of the bonded atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. From the BP and LP interactions we can predict both the relative positions of the atoms and the angles between the bonds, called the bond angles The angle between bonds. Each group around the central atom is designated as a bonding pair (BP) or lone (nonbonding) pair (LP). In the VSEPR model, the molecule or polyatomic ion is given an AX mE n designation, where A is the central atom, X is a bonded atom, E is a nonbonding valence electron group (usually a lone pair of electrons), and m and n are integers. That is, the one that minimizes repulsions. Groups are placed around the central atom in a way that produces a molecular structure with the lowest energy.
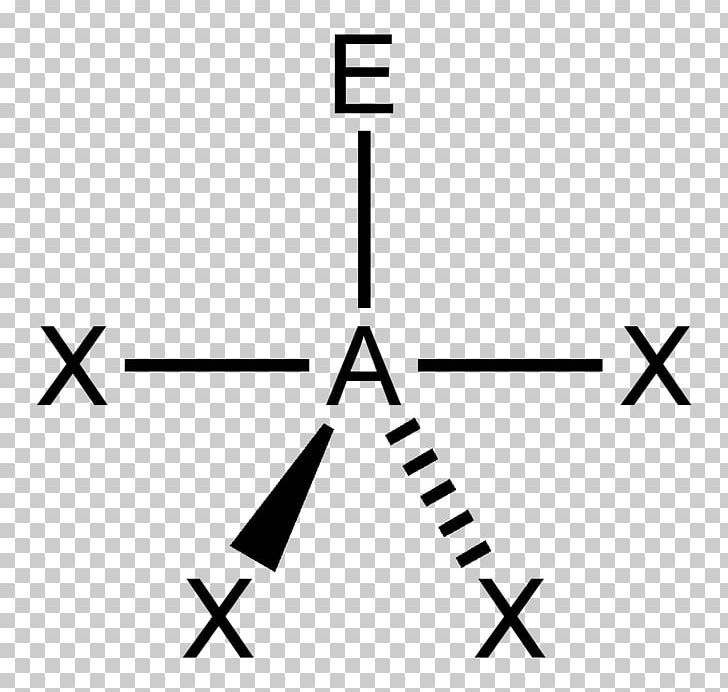
Following sections of this will connect the VSEPR model to molecular orbitals.įigure 6.3.2 Geometries for Species with Two to Six Electron Groups A more sophisticated treatment of bonding is needed for systems such as these. Instead, many of these species, including SrF 2 and BaF 2, are significantly bent. More disturbing, the VSEPR model predicts that the simple group 2 halides (MX 2 ), which have four valence electrons, should all have linear X–M–X geometries.

The hybrid orbital picture, although more complex, provides a better explanation of such things In this section we will make the connection between hybrid orbital described in Chapter 6.2 and VSEPR. In fact, structural studies have shown that the H–S–H and H–P–H angles are more than 12° smaller than the corresponding bond angles in H 2 O and NH 3. It predicts, for example, that H 2 S and PH 3 should have structures similar to those of H 2 O and NH 3, respectively. Although the VSEPR model is a simple and useful method for qualitatively predicting the structures of a wide range of compounds, it is not infallible. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. (pronounced “vesper”), which is simple to use to predict the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions. We continue our discussion of structure and bonding by introducing the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model A model used to predict the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions, based on the idea that the lowest-energy arrangement for a compound is the one in which its electron pairs (bonding and nonbonding) are as far apart as possible. To predict whether a molecule has a dipole moment.To use the VSEPR model to predict molecular geometries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
